Adversarial Online Learning with Variable Plays in the Pursuit-Evasion Game: Theoretical Foundations and Application in Connected and Automated Vehicle Cybersecurity
Published in IEEE Access, 2021
Abstract
We extend the adversarial/non-stochastic multi-play multi-armed bandit (MPMAB) to the case where the number of arms to play is variable. The work is motivated by the fact that the resources allocated to scan different critical locations in an interconnected transportation system change dynamically over time and depending on the environment. By modeling the malicious hacker and the intrusion monitoring system as the attacker and the defender, respectively, we formulate the problem for the two players as a sequential pursuit-evasion game. We derive the condition under which a Nash equilibrium of the strategic game exists. For the defender side, we provide an exponential-weighted based algorithm with sublinear pseudo-regret. We further extend our model to heterogeneous rewards for both players, and obtain lower and upper bounds on the average reward for the attacker. We provide numerical experiments to demonstrate the effectiveness of a variable-arm play.
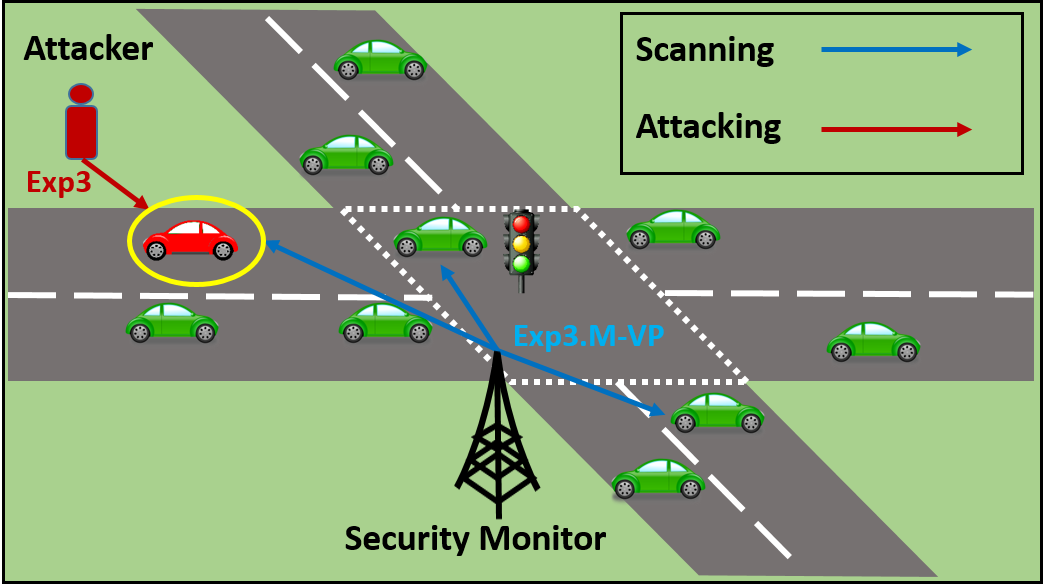 |
|---|
| A pursuit-evasion game scenario where a malicious attacker who adopts Exp3 compromises the red vehicle, and a security monitor as defender who adopts Exp3.M-VP scans the red vehicle as well as two other vehicles. The pursuit-evasion game is conducted in a sequential manner. |
